- Title
- Micro sensors for accurate on-site monitoring of airborne nanoparticles
- Date
- 2021.06.11
- Writer
- 기계공학부
- 게시글 내용
-
Micro sensors for accurate on-site monitoring of airborne nanoparticles
For accurate monitoring of airborne nanoparticles at a point of care, a Yonsei research team led by Professors Kim, Yong-Jun developed micro nanoparticle detection sensors. These sensors grow nanoparticles to micrometer droplets in the chip through condensation, and count grown droplets based on the light scattering method. Using this measurement principle, the sensors were able to count individual nanoparticles as small as 10 nm, guaranteeing accurate measurement performance. Moreover, since the essential functions for growing droplets are integrated on a single chip using semiconductor manufacturing process, the sensors are far cheaper, smaller than the conventional nanoparticle instruments.
According to professor Kim, the sensors can be readily used in any kinds of environments where on-site monitoring is required, such as indoors, outdoors or work places. Also, they can be applied to the assessing individual daily exposure to nanoparticles, contributing to the undergone exposome projects including ‘The Human Early-Life Exposome (HELIX)’. The results of the research were published on 2018, November 5 as the article of the Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, and 2020, March 1th as the article of RSC Lab on a chip. (Link to the paper)

Figure 1: The two types of micro nanoparticle detection sensors; left one generate droplets using butanol vapor (Atmos. Meas. Tech., 12, 5335–5345, 2019), and the other is based on water vapor (Lab Chip, 2020, 20, 1092). The essential components for growing droplets on the chip, which are integrated on the single chip using the semiconductor manufacturing process.
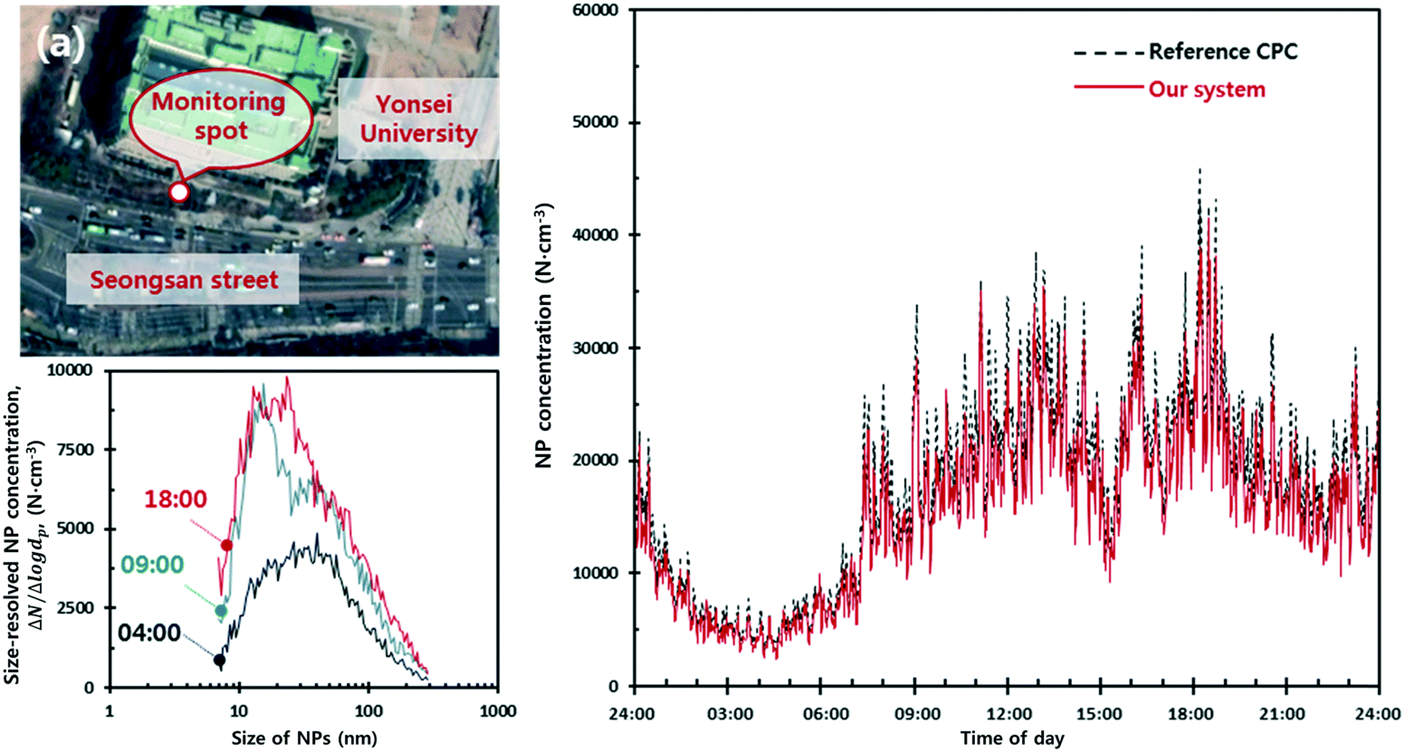
Figure 2: On-site monitoring results of the sensors, compared with the reference instrument.

