연세대학교 화공생명공학과 함승주 교수 연구팀이 다양한 감염 바이러스를 신속 정확하며 높은 처리량을 가지는 방식으로 진단 가능한 융합 나노 센서를 개발했다.
지난 20년간 신 변종 바이러스 감염병의 유행이 발생하고 있으며, SARS-CoV-2에 의해 발생한 코로나 바이러스 감염증 2019(COVID-19)는 전 세계 인구의 건강, 사회, 그리고 경제에 파괴적인 영향을 미치고 있다. 이에 따라 새로운 바이러스에 의한 감염병 발병과 초기 바이러스 확산을 완화시키기 위한 고급 진단 기술의 개발과 광범위한 테스트가 필요하며 이를 구현하기 위한 많은 노력이 요구된다.
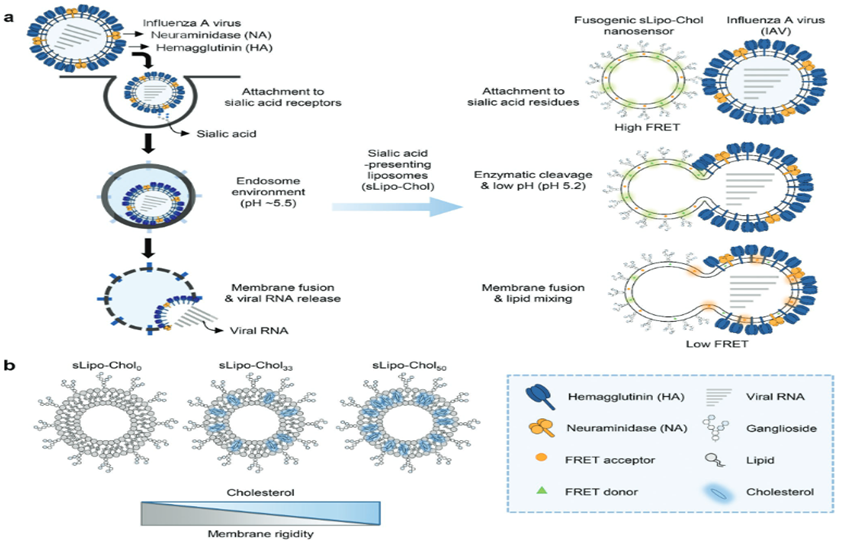
본 연구팀에서는 생체 모방한 리포좀-콜레스테롤 기반의 융합 나노 센서를 이용하여 인플루엔자 A 바이러스의 선택적이고 민감한 검출이 가능한 형광 분석 기술을 개발했다. 본 융합 생체 모방 나노 센서는 인플루엔자 A 바이러스의 감염에 대한 구조적 특징과 분자 상호작용에 대한 이해를 바탕으로 디자인 되었으며, 나노 센서와 인플루엔자 A 바이러스의 막 융합에서 생성된 형광 신호를 정량적으로 검출하도록 구현되었다.
특히, 나노구조체 막 강성과 유동성 조절을 통해 나노 센서의 융합 효율을 향상시켜 표적 바이러스가 있을 때 증폭된 형광 신호를 유도할 수 있다는 것을 입증했다. 낮은 막 강성을 가진 리포좀은 바이러스에 대해 더 민감한 융합 활성도를 나타내면서, 높은 막 강성을 가진 리포좀보다 더 낮은 검출 한계에 도달함을 나타냈다.
또한, 본 융합 생체 모방 나노 센서는 실제 조류 분변 샘플에서 다양한 인플루엔자 A 바이러스 하위 유형에 대한 고민감 및 특이적 검출도 나타내 감지 성능의 신뢰성과 경고성을 나타냈다.
따라서 이번 연구를 통해 RNA의 추출 및 정제 없이 온전한 인플루엔자 A 바이러스의 정량적 검출이 가능할 뿐만 아니라 세계 인구의 생명을 위협하는 신흥 감염 바이러스에 대한 신속한 검출과 대응을 위한 큰 잠재력을 기대할 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
이번 연구 성과는 교육부에서 추진하는 이공학학술연구기반구축사업, 과학기술정보통신부에서 주관하는 개인기초연구사업, 신변종감염병대응플랫폼핵심기술개발사업, 환경부에서 추진하는 생물학적위해인자관리기술개발사업의 지원으로 함승주 교수 연구팀의 박채원 박사 (제 1저자)와 인천대 김은정 교수 (제 1저자)가 함께 진행됐으며, 세계적인 과학 분야 권위지 (IF=19.924) ‘Advanced Functional Materials’에 4월 29일자(현지시간)로 게재됐다.
A research team led by Professor Seung-Joo Ham of Yonsei University's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed a fused nano sensor that can diagnose various infectious viruses in a rapid, accurate, and high-throughput manner.
Over the past two decades, an epidemic of novel viral infectious diseases has been occurring, and the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 has had a devastating impact on the health, society, and economy of the world's population. This calls for the development and widespread testing of advanced diagnostic technologies to mitigate outbreaks of infectious diseases caused by new viruses and the initial spread of viruses.
In this study, the research team developed a fluorescence assay for the selective and sensitive detection of influenza A virus using liposome-cholesterol fused biomimetic nanosensors. The fused biomimetic nanosensor was designed based on the understanding of the structural features and molecular interactions of influenza A virus infection and was implemented to quantitatively detect the fluorescence signal generated by the membrane fusion of the nanosensor and influenza A virus.
In particular, the authors demonstrated that the fusion efficiency of the nanosensor can be improved by controlling the nanostructure membrane stiffness and fluidity to induce an amplified fluorescence signal in the presence of the target virus. Liposomes with low membrane stiffness exhibited more sensitive fusion activity against viruses, while reaching lower detection limits than liposomes with high membrane stiffness.
In addition, the fused biomimetic nanosensor also exhibited distress and specific detection of different influenza A virus subtypes in real bird fecal samples, indicating the reliability and alertness of its detection performance.
Therefore, this study not only enables quantitative detection of intact influenza A virus without extraction and purification of RNA, but also has great potential for rapid detection and response to emerging infectious viruses that threaten the lives of the world's population.
This research was supported by the Ministry of Education's Science and Engineering Academic Research Infrastructure Construction Project, the Ministry of Science and ICT's Personal Basic Research Project, the New Variant Infectious Disease Response Platform Core Technology Development Project, and the Ministry of Environment's Biological Hazard Management Technology Development Project. This research was conducted with Dr. Chae-Won Park (first author) from Professor Seung-Joo Ham's research team and Professor EunJeong Kim (first author) from Incheon University was published on April 29 (local time) in the world's leading scientific journal “Advanced Functional Materials” (IF=19.924).
Advanced Functional materials (2023) (IF: 19.924)
Published: 29 April 2023
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202214603