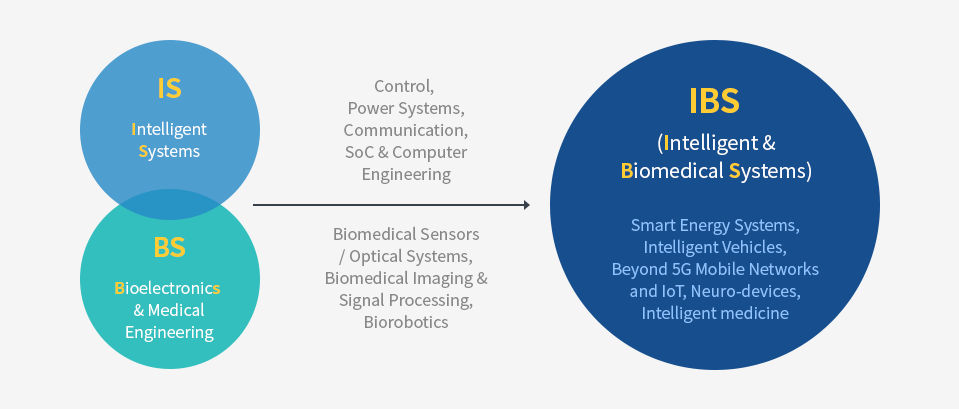
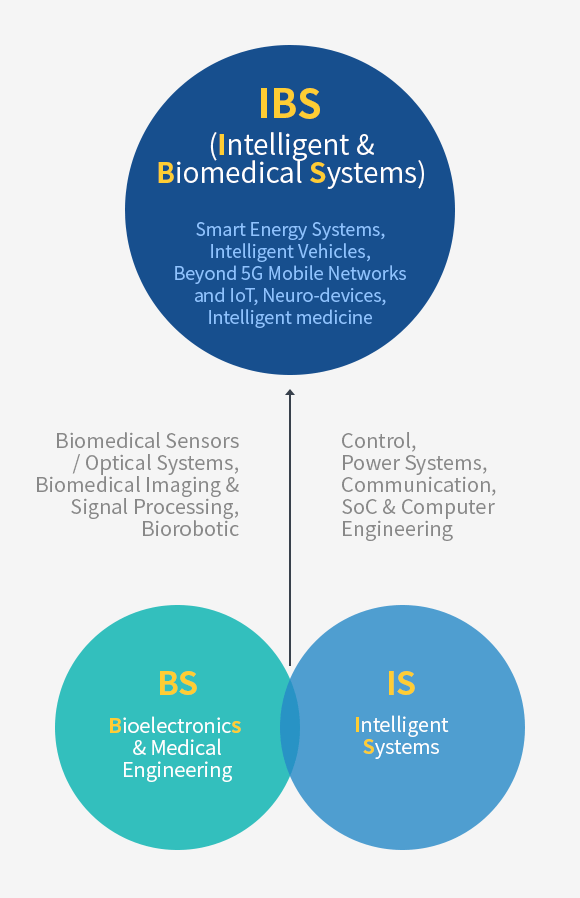
The Intelligent and Biomedical Systems group leads the development of intelligent electronics and bioelectronic medical systems. The IBS includes two sub-groups, Intelligent Systems (IS) and Bioelectronics and Medical Engineering (BME). The IS research combines control and power systems, communications, and compute engineering into multidisciplinary themes encompassing smart energies, intelligent traffic systems, next-generation internet and communication technologies, and future computing systems. The BME group is on the leading edge of devising biosensors, medical imaging, and robotics that are applied to medicine and biology. The faculty of BME also leads research collaboration with the College of Medicine located in the same campus of Yonsei University.

Intelligent Systems (IS)

Intelligent systems are adaptive, self-trainable systems that process large amount of data to solve complicated problems. The IS group tackles various challenges in devising intelligent systems. This group is further divided into four sub-groups, Smart Energy Systems, Intelligent Computing, and 5G Mobile Networks and IoT. Undergraduate courses relevant to IS research include Basic Circuit Theory, Signals and Systems, Digital Logic Circuits, Control Engineering, Electrical Power Systems, Power Electronics, Communications Theory, and Computer Architecture. The following table lists the faculty members of Intelligent Systems.
Smart Energy Systems

Smart energy systems (a.k.a. smart grid) deals with all aspects of electricity such as energy generation and distribution, grid intelligence, renewable energy, electrical transportation, and energy-efficient building. The research topics of smart energy systems range from energy-harvesting devices to large utility systems and micro-grids. The advance of renewable energy will have a profound impact on the global society since modern economy demands increasing amount of energy production and thus requires sustainable energy sources. Related undergraduate courses are Electrical Power Systems, Power Electronics, and Electric Machines and Control.
Intelligent Computing
| Intelligent Vehicles | Intelligent systems are adaptive, self-trainable systems that process large amount of data to solve complicated problems. The IS group tackles various challenges in devising intelligent systems. This group is further divided into four sub-groups, Smart Energy Systems, Intelligent Computing, and 5G Mobile Networks and IoT. Undergraduate courses relevant to IS research include Basic Circuit Theory, Signals and Systems, Digital Logic Circuits, Control Engineering, Electrical Power Systems, Power Electronics, Communications Theory, and Computer Architecture. The following table lists the faculty members of Intelligent Systems. |
|---|---|
| Beyond 5G Mobile Networks & IoT | Internet of Things (IoT) has sparked data explosion by connecting a massive number of sensors and devices in cloud computing and networking environments. Next-generation communication systems beyond 5G will feature machine-to-machine connections and offer low-power, low-latency, massively parallel, reliable, and secure connections. The applications of future mobile networks include augmented or virtual reality, tactile internet, sensor networks, connected cars, cloud computing, smart homes, and many more. Related undergraduate courses are Communications Theory, Digital Communications, Computer Networks, and Embedded and Digital Systems Design. |
The evolution of computing systems is transforming the society and IT industry. Intelligent Computing drives recent research thrust for machine learning, autonomous driving, Internet of Things, mobile and cloud computing, etc. Computer architecture and VLSI research form the core of intelligent computing, which provides a vehicle for faster, low-power, and reliable computing of exploding data. Relevant undergraduate courses include Digital Logic Circuits, Data Structures and Algorithms, Computer Architecture, Microprocessors, Operating Systems, Digital Systems Design, and Embedded Systems Lab.
The core faculty members of intelligent system are listed below.
Bioelectronics and Medical Imaging (BME)

Bioelectronics and medical imaging are leading-edge technologies that study human bodies and biological objects. Research topics include biomolecular images, bio-chips, bio-signal processing, medical imaging (e.g., magnetic resonance imaging, MRI), X-ray imaging, computed tomography (CT), and ultrasound. Related undergrate courses include Basic Circuit Theory, Signals and Systems, Electromagnetics, Digital Signal Processing, and Bioelectronics. The faculty members of BME are listed below.
| No. | Research Labs | Faculty | Locations | Extensions | Emails |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flexible Electronic Device Lab | Ahn, Jong-Hyun | C310 | 2776 | ahnj@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 2 | Mixed-Signal IC Lab | Chae, Youngcheol | B712 | 2866 | ychae@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 3 | Medical Artificial Intelligence Lab | HWANG, Dosik |
C618 |
5771 | dosik.hwang@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 4 | Biological Cybernetics Lab | KIM, DaeEun | C622 | 5879 | daeeun@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 5 | Biophotonics Engineering Lab | KIM, Donghyun | C723 | 2777 | kimd@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 6 | Medical Imaging Lab | KIM, Dong-Hyun | C228 | 5874 | donghyunkim@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 7 | Radio Frequency & Analog Circuit Design Lab | KIM, Tae Wook | C620 | 5770 | taewook.kim@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 8 | Multidimensional Insight Lab | LEE, Sanghoon | C715 | 2767 | slee@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 9 | Nano Device Lab | LEE, Taeyoon | C312 | 5767 | taeyoon.lee@yonsei.ac.kr |
| 10 | Functional Bio-integrated Electronics and Energy Management Lab | Yu, Ki Jun | C224 | 2769 | kijunyu@yonsei.ac.kr |
Bioelectronics
Medical Engineering applies electrical engineering techniques to human bodies. For instance, machine learning is used in Medical Engineering for medical image generation, analysis, and diagnosis. Medical information and bio-signals are trained and obtained from the artificial intelligence. Electronic circuits are also used for the local amplification and multiplexed reading of signal measurement. Bio-implantable devices are also important topics of Medical Engineering. Devising bio-implantable devices requires a careful selection of materials that can support high-performance operations with great lifetime reliability.
Medical Imaging
Optical imaging and sensing techniques help identify, visualize, and quantify molecular processes in biomedical applications. Examples are electrical property imaging, metal artifact correction, view-angle tilting techniques. Multi-modal medical imaging approaches are used to overcome the current limitations of imaging systems, e.g., MRI, CT, etc. The real-time imaging capability of ultrasound machines has been incorporated into MRI systems to handle motion corruption. Multi-echo-based acquisition and processing enabled the construction of ultra-high-resolution brain images, etc.